A significant outbreak of the Chikungunya Virus is currently unfolding in Southern China, raising concerns about the rapid spread of this mosquito-borne illness in a region with little pre-existing immunity. The primary area affected is Foshan, a major manufacturing hub, where over 7,000 cases have been reported, marking it as the largest outbreak ever documented in mainland China, according to a recent report from PBS News. This situation underscores the importance of understanding the virus, its symptoms, and the measures being taken to control its spread.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Chikungunya Virus
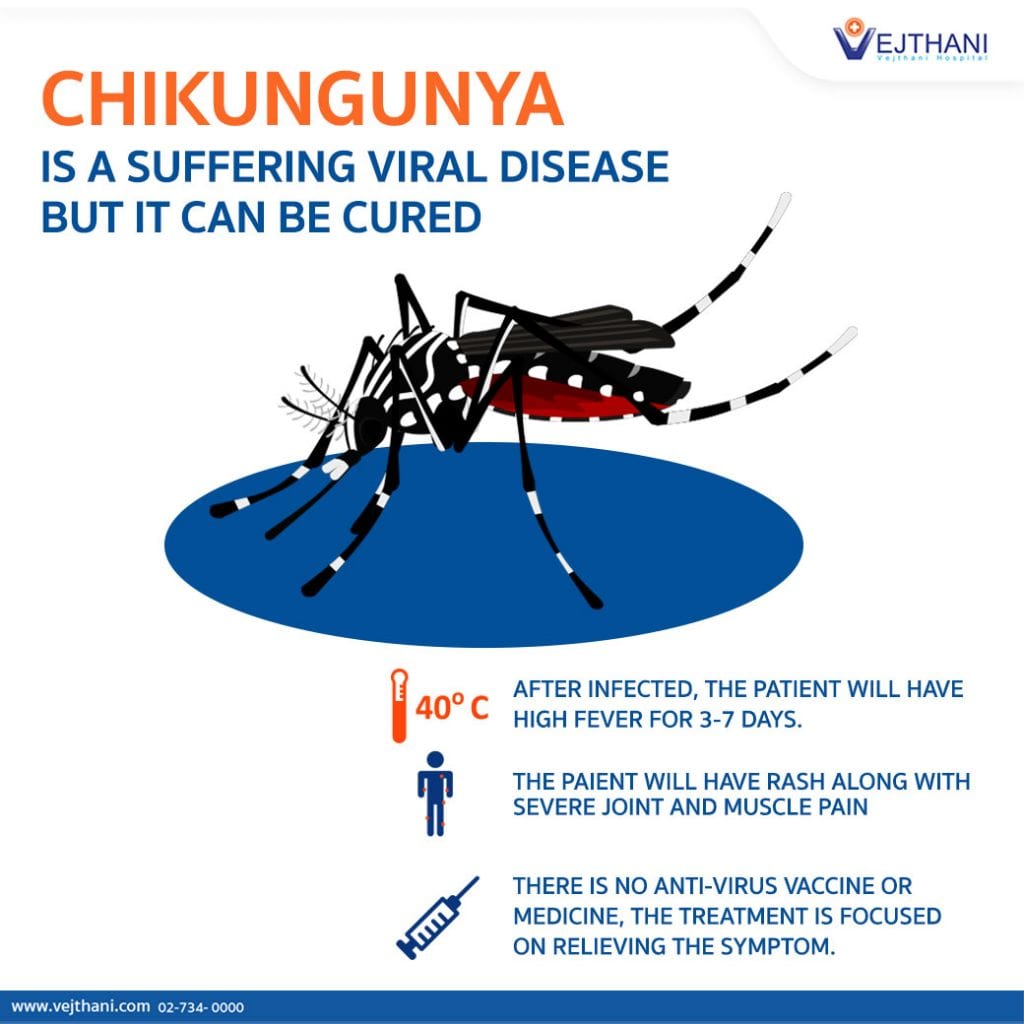
Chikungunya is transmitted through the bites of infected Aedes mosquitoes, the same vectors responsible for spreading Zika and dengue viruses. The disease is characterized by a range of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. These symptoms, as outlined by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), typically include:
- Fever
- Muscle pain
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Rash
- Debilitating joint pain
While severe cases are rare, and deaths even rarer, infants and the elderly, particularly those with underlying health conditions, are at higher risk of complications. The joint pain associated with Chikungunya can be particularly debilitating, often persisting for months or even years after the initial infection.
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for Chikungunya. Management focuses on alleviating symptoms through medication, rest, and supportive care. Two vaccines have been approved in some regions, primarily for travelers, but their widespread availability in affected countries remains limited.
The Outbreak in Southern China: A Closer Look
The scale of the Chikungunya outbreak in Foshan, Southern China, is unprecedented for the region. The lack of prior exposure to the virus within the population has created a highly susceptible environment, allowing for its rapid dissemination. The PBS News report highlights that this is the largest outbreak in mainland China.
The Chinese authorities have responded with a series of aggressive control measures aimed at curbing the spread of the virus. These measures include:
- Distribution of Mosquito Nets: Providing a physical barrier against mosquito bites, particularly during peak activity periods.
- Insecticide Spraying: Targeting mosquito populations in residential areas and public spaces to reduce their numbers.
- Drone Surveillance: Utilizing drones to identify and eliminate stagnant water sources, which serve as breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
- Biological Control Methods: Introducing “elephant mosquitoes,” which prey on virus-carrying mosquitoes, and mosquito-eating fish into local ponds to naturally regulate mosquito populations.
Furthermore, strict protocols have been implemented in Foshan, including mandatory hospitalization for confirmed patients for at least seven days or until they test negative for the virus. Home inspections are also being conducted to eliminate stagnant water sources, with fines imposed for non-compliance.
Travel Advisory and Precautions
In light of the ongoing outbreak, the U.S. CDC has issued a Level 2 travel advisory for Southern China, urging visitors to exercise increased caution. This advisory recommends the following precautions:
- Enhanced Mosquito Bite Prevention: Using insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, IR3535, oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE), para-menthane-diol (PMD), or 2-undecanone.
- Wearing Protective Clothing: Covering exposed skin with long-sleeved shirts and pants.
- Staying in Air-Conditioned or Screened Accommodations: Reducing exposure to mosquitoes indoors.
The Importance of Vector Control
Effective vector control is crucial in preventing the spread of Chikungunya and other mosquito-borne diseases. Integrated vector management strategies, combining various methods such as source reduction, larviciding, and adulticiding, are essential for achieving sustainable control. Community participation and education are also vital components of successful vector control programs.
The Global Threat of Emerging Viruses
The Chikungunya outbreak in Southern China serves as a reminder of the ongoing threat posed by emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Factors such as climate change, urbanization, and increased international travel contribute to the spread of these diseases, highlighting the need for robust surveillance systems, rapid response mechanisms, and international collaboration to prevent and control outbreaks.
As noted by health officials, the Foshan outbreak underscores the importance of proactive public health measures, including vector control, community engagement, and public awareness campaigns, to mitigate the impact of emerging infectious diseases. Continued research and development of vaccines and antiviral therapies are also crucial for enhancing our preparedness and response capabilities.
Conclusion
The Chikungunya virus outbreak in Southern China highlights the potential for rapid spread of mosquito-borne illnesses in susceptible populations. The aggressive control measures implemented by Chinese authorities, along with travel advisories from organizations like the CDC, underscore the seriousness of the situation. Vigilance, prevention, and continued research are essential to manage and mitigate the impact of this and future outbreaks.
